Broadly speaking, energy storage is the gathering of energy produced at one time, to be stored and used at a later time. For energy storage systems (ESS) there are two major use cases: creating utility-independent, solar-powered homes (residential ESS) and – on a larger scale – utilities supplementing generated power during periods of high demand (utility scale ESS).
Older generation residential solar energy systems are tied to the utility power grid via inverters which convert power from solar panels to AC electrical power during daylight hours. Marketable excess power might be sold back to utility companies. However, during the hours of darkness the end user is relying on the utility’s electricity supply. Utility companies are aware of these limitations and adjust their pricing models accordingly. Residential customers pay based on so called “time-of-use” rates which are higher when solar power is not available.
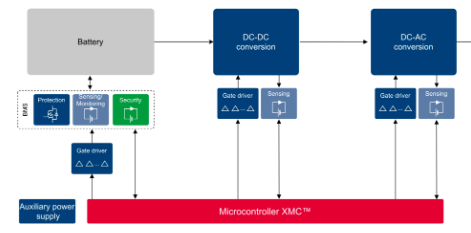
This is where behind-the-meter ESS comes into play. The electricity that is collected via solar panels charges batteries – the energy is stored. When using these batteries with an inverter, the demand for AC power can be fulfilled at any time.